V2 = 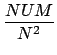
|
(5) |
The fringe detector uses a four bin algorithm with path length modulation. See Colavita (1999) for a detailed description of this method. The detector array is read 5 times, before the modulation starts and after each quarter-wave of modulation. These reads are called z, a, b, c and d. Each of these reads consists of a number of sub-reads to reduce the effective read-noise. The basic output of the fringe detector, which is called a sample (Sec. 2.2), is the array counts for each channel and these values are read in by Kvis.
For each channel the integrated flux in each bin is calculated as
| A = (a - z)/ns | B = (b - a)/ns | ||
| C = (c - b)/ns | D = (d - c)/ns, | (1) |
and the total flux is
A measure of the energy is given by| NUM = X2 + Y2. | (4) |
|
|
(6) |